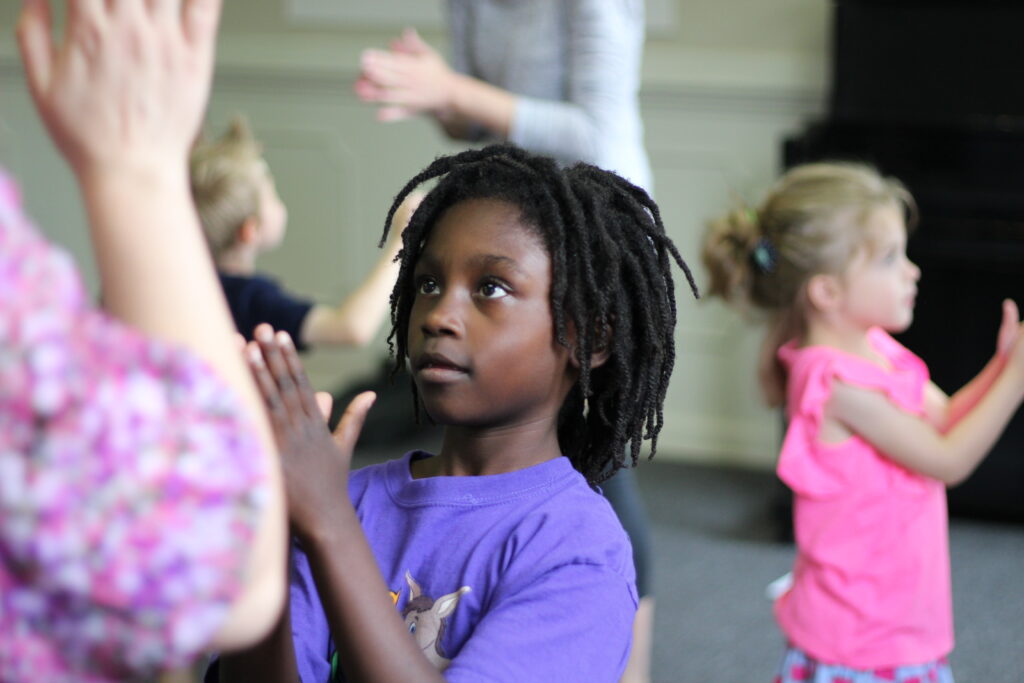Parents and teachers alike understand the challenges that screen time poses to children as well as adults. Prior to the Covid pandemic, kids ages 8-18 were spending up to 7.5 hours on average in front of a screen for entertainment. More than half of that time was spent watching television. COVID-19 and the lock-down made matters even worse. Despite the need to attend online classes for school, overall digital device usage increased by 5 hours, with adolescents averaging even higher at 8 hours a day.
As our children’s screen time has increased substantially over the past decade, the ill effects of it on the physical and mental well-being is being studied more and more. Pediatric health professionals and children’s educators alike highly recommend other means of entertainment for children to offset this epidemic. Children’s music education is one such means of entertainment that helps reduce screen time.
The Health Effects of Screen Time in Children
Children’s health professionals point to many issues that may arise in children that are exposed to an excessive amount of screen entertainment:
- Impaired emotional and social intelligence.
- Sleep deprivation and disturbed sleep cycles.
- Mood problems such as irritability, depression, anxiety, and ADHD.
- Poor self-image, weight problems, and body image issues.
- Vision issues such as eye strain and myopia.
- Neck pain and carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Social isolation and fear of missing out (FOMO).
- Phantom Vibration Syndrome, where a person imagines their phone is ringing or vibrating when it’s actually not.
- Obsessive, excessive, compulsive, and impulsive use of digital devices.
Children’s Music Education to Reduce Screen Time
Pediatric health care professionals recommend exposing children to other activities to reduce their screen time as well as increase their interests in other entertainment. Teachers of children’s music education have long known the positive impacts that music classes have on a child’s well-being during their developmental years and beyond:
- Improved motor skills and hand-eye coordination.
- Increased self-awareness and social skills.
- Greater patience and resiliency in problem solving.
- Better physical health, sleep habits, and appetite.
- Elevated self-motivation, prioritization, and time management skills.
- Improved moods and abstract creativity.
- Accelerated language and writing comprehension skills.
It is clear that as technology increases at a greater and greater rate, it will compete for the attention of humans in developed societies. Children are even more susceptible to the negative impacts of excessive screen time in their developmental years. Supplemental music lessons offer an alternative to screen time while providing all of the benefits that music instruction offers to kids – including self-imposed limitation of screen time; increased problem-solving skills, time management and prioritization; increased self-awareness and social skills, and more.