Part 2 – Through THE MIND
Children’s piano instructors understand that a strong foundation in music from the earliest ages will help improve student’s progress and understanding of the keyboard later in childhood. We began by exploring how movement and the body influence this early instrumental preparation. As we continue to delve into how various areas of influence in early music education grooms children for the piano, or any musical instrument, we reveal how it prepares the MIND.
Early Childhood Music Education Prepares the Mind for Piano Lessons
Is there a purpose to learning an instrument or reading music if a child has not first absorbed musical thoughts? For a very long time, expressive body movement was not linked to higher brain function in formal education. Until as recently as 1995, researchers and educators limited the health benefits of movement and exercise solely to the body rather than the brain. Now it is clear that movement is not separate from higher brain function or development, and that expressive movement combines body functioning with affective areas of the brain such as imagination. These neural connections can be seen in language, literacy, and dominance of ear.
- Learning Musical Language through Songs and Singing – It is easy to understand that children would not be asked to speak a language they have not heard, nor read a language they cannot speak. It stands to reason that there should be no exception for listening to and “speaking the language of music” before learning an instrument. Asking a child to read and sing or play a song on an instrument before they have ever heard it would not give it meaning of familiarity and affinity. This could be one reason why so many young piano students learn to play only “notes” instead of expressing musical ideas. The large repertoire of songs children have sung with friends and family as well as in the early childhood education classroom equips them with a musical language that will eventually allow them to better learn and play an instrument such as piano.
- Childhood Music Education Provides Foundation in Music Literacy – Through moving and singing children gain a multitude of experience with rhythmic patterns and steady beat, as well as tonal patterns and home tone. Just as a child learning to read looks for familiar patterns in words and sentences, so do they seek rhythmic and tonal patterns in music. This familiarity with musical motifs enable children to better express musical ideas, as their literacy brings harmony to mind and spirit. The ability to better grasp the patterns and language of a musical instrument is also influenced by dominance of ear.
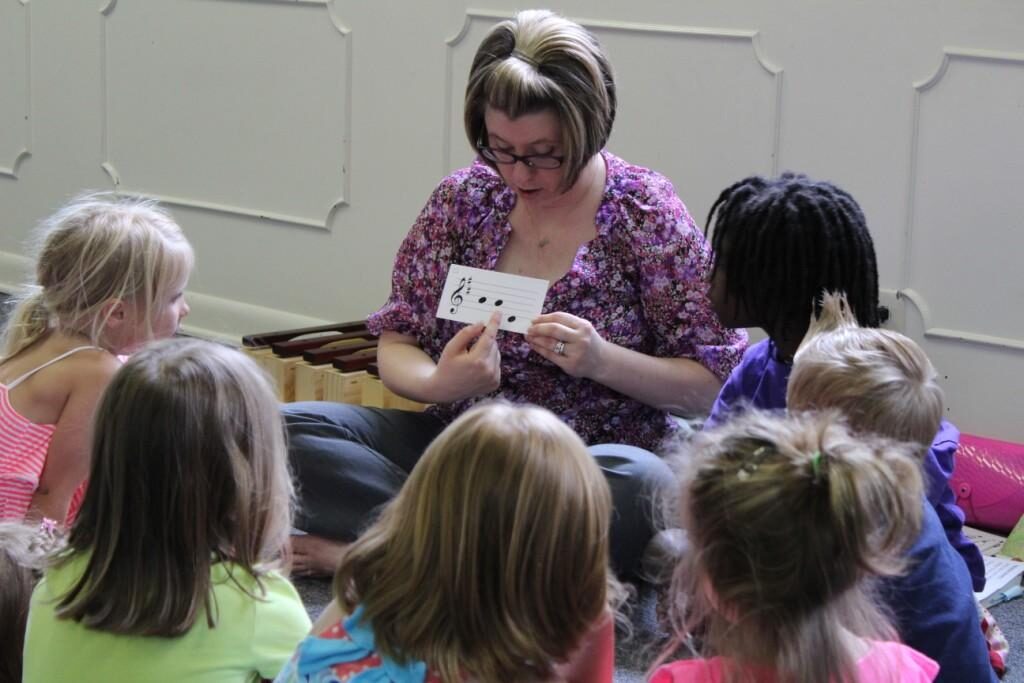

- Listening Skills and Dominant of Ear in Learning Piano – Children who have participated in early music education have learned to be led musically by their ears. Piano teachers discover that they have better listening skills and aural preparation, allowing the eye to more easily recognize what the ear already knows. As one of the first senses to develop in the womb, the ear is dominant in early childhood as children learn language and familiar sounds. Discriminatory listening skills develop as they attune to important sounds in the environment, such as a mothers voice. Early childhood education programs promote these aural insights by teaching children to focus tentatively on a sound source while imitating sounds vocally. Understanding slight distinctions in sound is a vital foundation for all learning.
The ear, arguably the most vital sensory channel to most children’s learning, is the linchpin for Listening, speaking/singing, and balanced/coordinated movement. It is no wonder that early childhood music education is so vitally important in learning an instrument such as piano since music links the ear, the voice, and the body.
This commentary is based on the article The Well-Prepared Beginner: Prepared in Body, Mind, Spirit, and Family by Lorna Heyge, Ph. D. Dr. Heyge is a pioneer in childhood music instruction, as well as a piano teacher of many years.