Our series on how early childhood music programs influence Music Literacy at the Keyboard continues with the importance of body movement with music and listening. We have explored how singing a repertoire of familiar songs, as well as setting a good foundation of keyboard posture, are vital to instrumental education. Now the close relationship between music and movement complements these footings toward success in music literacy.
The Connection Between Music and Movement
Cultures all across the globe have used movement as the body’s expression of rhythm, which shapes the way we use and understand language. Children naturally desire and enjoy movement because it is exhilarating and energizing. A good foundation of understanding body manipulation helps them to play an instrument expressively.
Listening is vital to nearly all learning, not the least music education. And just as controlling body movement is more challenging for children today, so is learning to listen well. Developing a “listening ear” must compete with the increased amount of noise/sound and visual stimulation in a child’s environment.
Listening and movement are closely aligned through the ears two major functions. The first is vestibular, which controls balance, and thus nearly all movement. The second is the auditory, which directs hearing and voluntary listening. Therefore, it is vital to establish the important link between those two functions in early childhood music education.

How Movement Benefits Early Childhood Music Education
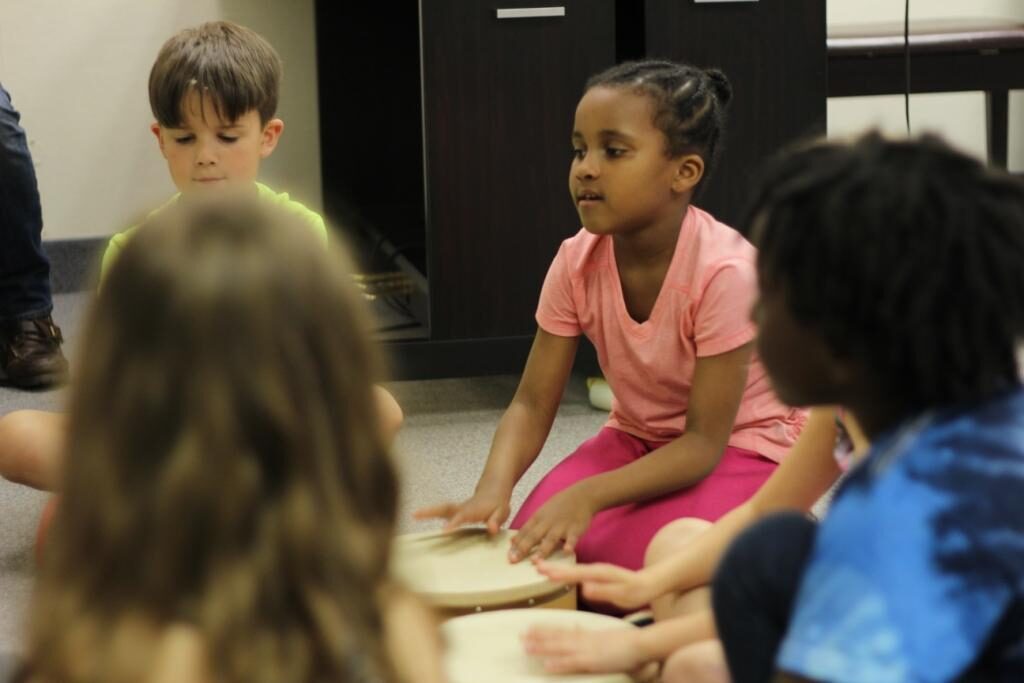
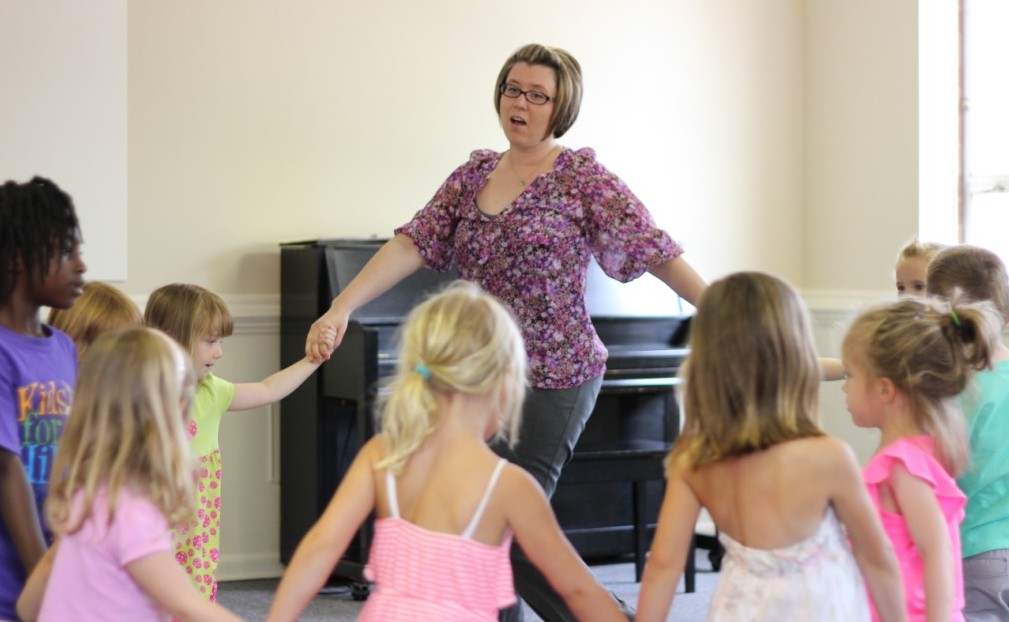
Rhythm and beat competency are emphasized in movement activities in early childhood music classes, particularly through tapping and drumming. Clapping, tapping one’s body, or using instruments such as rattles, sticks, bells or drums while singing helps to develop a child’s rhythm and beat. These, along with other group activities such as passing a beanbag in a song circle, brings children joy and social fulfillment. Drumming, in particular, has been a unique attraction for young and old alike in cultures all across the world. The tactile use of hands provides muscular memory while reinforcing the idea that the sound produced is directly related to the quality of the touch.
Dancing to recorded music as a group also provides a good opportunity for children to experience the flow of music while connecting to the larger community of their peers and teachers. In the most successful children’s music curriculum, teachers repeat these movement activities early and often so that the child in time feels free to express themselves through movement.
Early Listening Skills Make Children Better Musicians
Listening is defined as giving attention with the ear with the purpose of hearing. With the constant assault of noise and sound in our environment today, active listening is extremely important in order for children to concentrate. The very best training for listening employs the use of singing, chanting, and body movement to make the aforementioned connection between the auditory and balance/movement functions in the ear. Therefore, children’s music curriculum and teachers will continually engage in listening activities such as singing, reciting, and listening to music. The music teacher also instructs children to develop a listening posture that allows them to hear the music in their heads. This is particularly helpful at the piano, where body posture and hand position and technique are important for learning the keyboard. Through modeling and encouragement, the successful teacher is demonstrating attentive listening both through movement and posture.
Establishing and reinforcing the important connection between movement and listening helps prepare young children for playing any instrument. The union they feel between singing, drumming, and dancing will support the transfer of their understanding to piano. By introducing the keyboard as an extension of the body in this way, children learn to play the instrument musically – feeling the total experience of the instrument.
In our final installment of this series about Music Literacy at the Keyboard, we will see how all of these different foundational music teaching tools set children on the deliberate Pathway to Literacy.
Much of the content for this post was based on the introduction to Music Makers: at the Keyboard, childhood music curriculum developed by Musikgarten.
Interested in knowing more about Musikgarten’s Music Makers: at the Keyboard material? Click this link to attend a Free information session.