The very title of this topic may seem provocative, as many childhood music educators and researchers have varying opinions on what makes a truly great children’s music instruction. There are various established and differing music teaching methods such as The Suzuki Method and The Orff Approach, or The Kodaly and Dalcroze methods. While some of these methods are more focused on the learning of an instrument, they all tend to share a core set of teaching principles. This is not a competitive comparison of any program versus another, but an analysis of the shared beliefs upon which most all music teachers and educators agree.
Core Principles of Children’s Music Education
Here are several basic, yet important tenants to teaching early childhood music education that can be found in nearly all successful children’s music programs:
Focus on the Child – This may seem blatantly obvious, but it is important to emphasize for all childhood educators not to lose the “forest from the trees,” by making the teaching method the center of attention instead of the child themselves. Focusing on the child requires a respect of each student and their individual learning journey. This important approach also touches on “Follow the Child,” one of the central principles of the celebrated Montessori teaching method.
Music and Movement – Research suggests that encouraging movement at an early age helps to improve all kinds of cognitive as well as physical development. The area of the brain associated with motor control, the cerebellum, is also largely responsible for our learning process. The connection of both music and movement release endorphins in the brain, which helps to maintain interest and energy in a subject. Finally, movement helps children with beat perception and the development of rhythm, timing, and the motor control that will assist in music comprehension and learning an instrument.
Parental/Caregiver Involvement in Children’s Music Education – One principle shared by nearly all successful early childhood music programs is the importance of parental participation. This is often graphically represented as a triangular relationship between child, teacher, and parent. As one would suspect, the importance of parental involvement is not only beneficial to music learning, but all kinds of learning and early childhood development. Research has shown that, just as with traditional academics, parental involvement is particularly beneficial in early children’s music programs through observation and mimicry, helping to develop a better understanding of cultural ties to music, musical concepts, group social interaction, and motor skills development through the use of musical instruments.
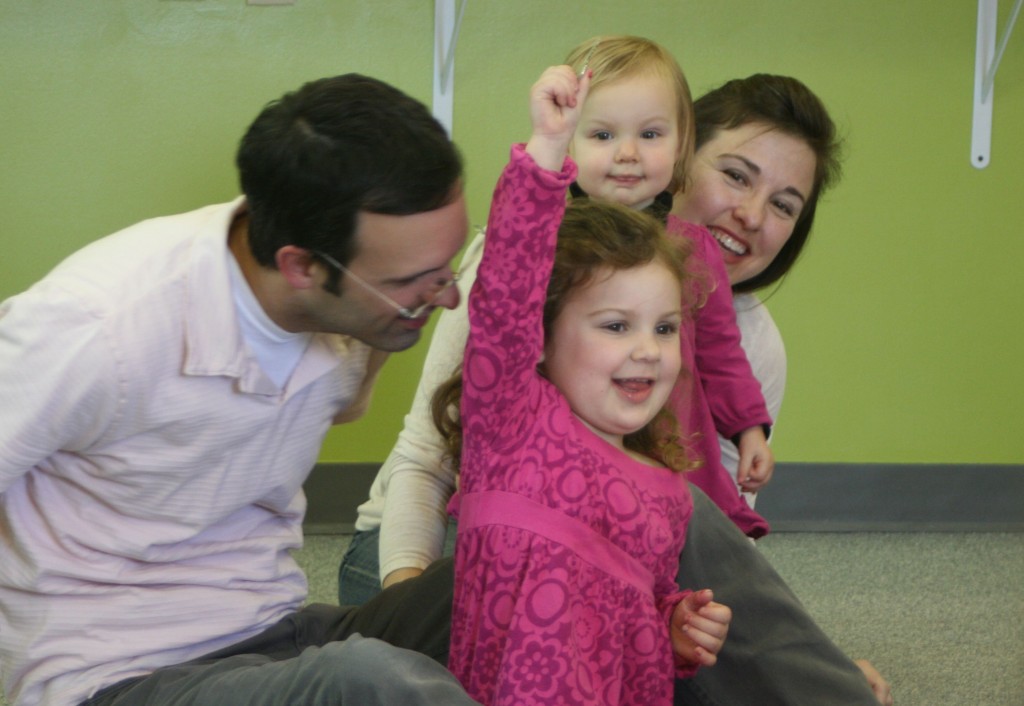

The most successful children’s music programs share several core principles that can be applied to nearly all early childhood learning. A Focus on the Child ensures that the approach respects the individuality and pace of learning that each child possesses. Music Combined with Movement helps with not only the mechanics of rhythm and timing of music, but also with cognitive aspects that encourage learning. Finally, Parental/Caregiver Involvement creates a triangular bond between teacher, child and parent which reinforces mimicry and a lifetime love of learning. All of these core principles combined with a carefully designed curriculum and supporting materials, are key to success for early childhood learning programs.